1. Layered Architecture (N-Tier Architecture)
- Description: Organizes software into layers where each layer provides services to the layer above it and depends on the layer below it.
- Examples:
Model-View-Controller (MVC): Separates data (Model), UI (View), and business logic (Controller).
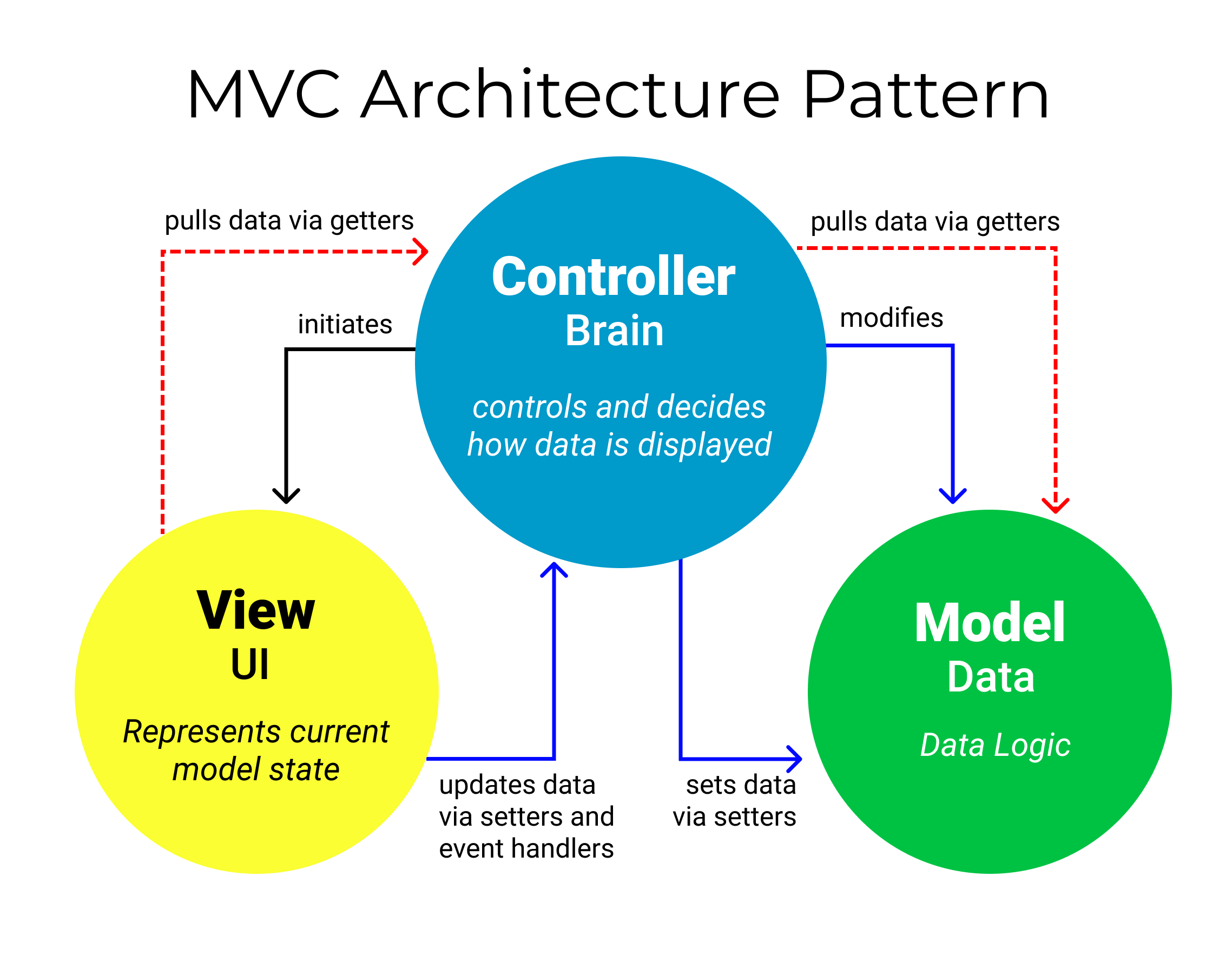
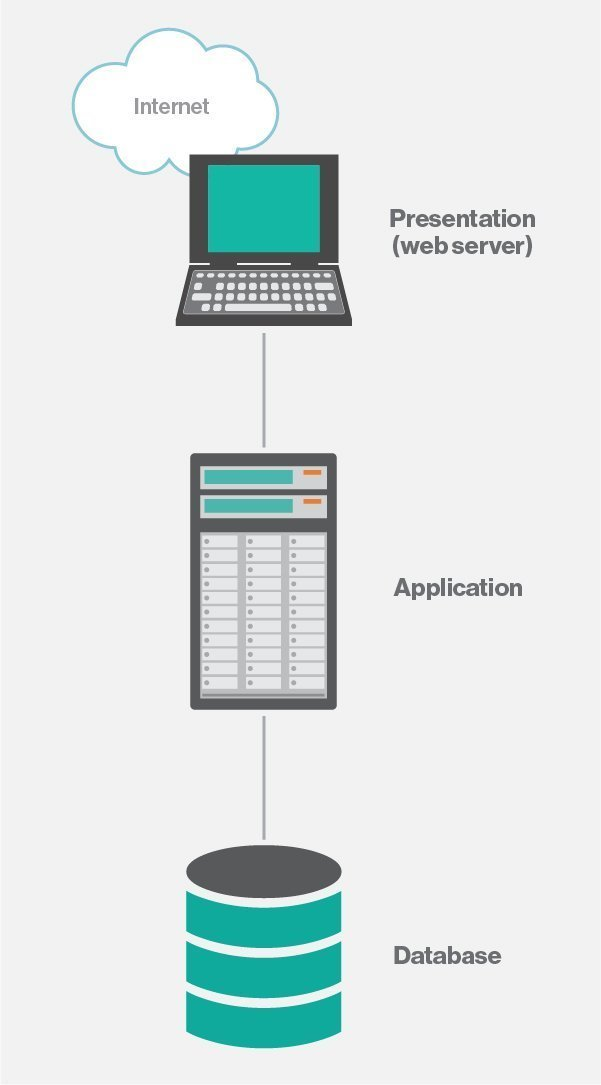
Three-Tier Architecture: Includes a Presentation Layer (UI), Business Logic Layer (Processing), and Data Layer (Database).
2. Microservices Architecture
- Description: Breaks down an application into small, independent services that communicate over a network.
- Examples:
E-commerce Platform: Separate services for orders, payments, users, and inventory.
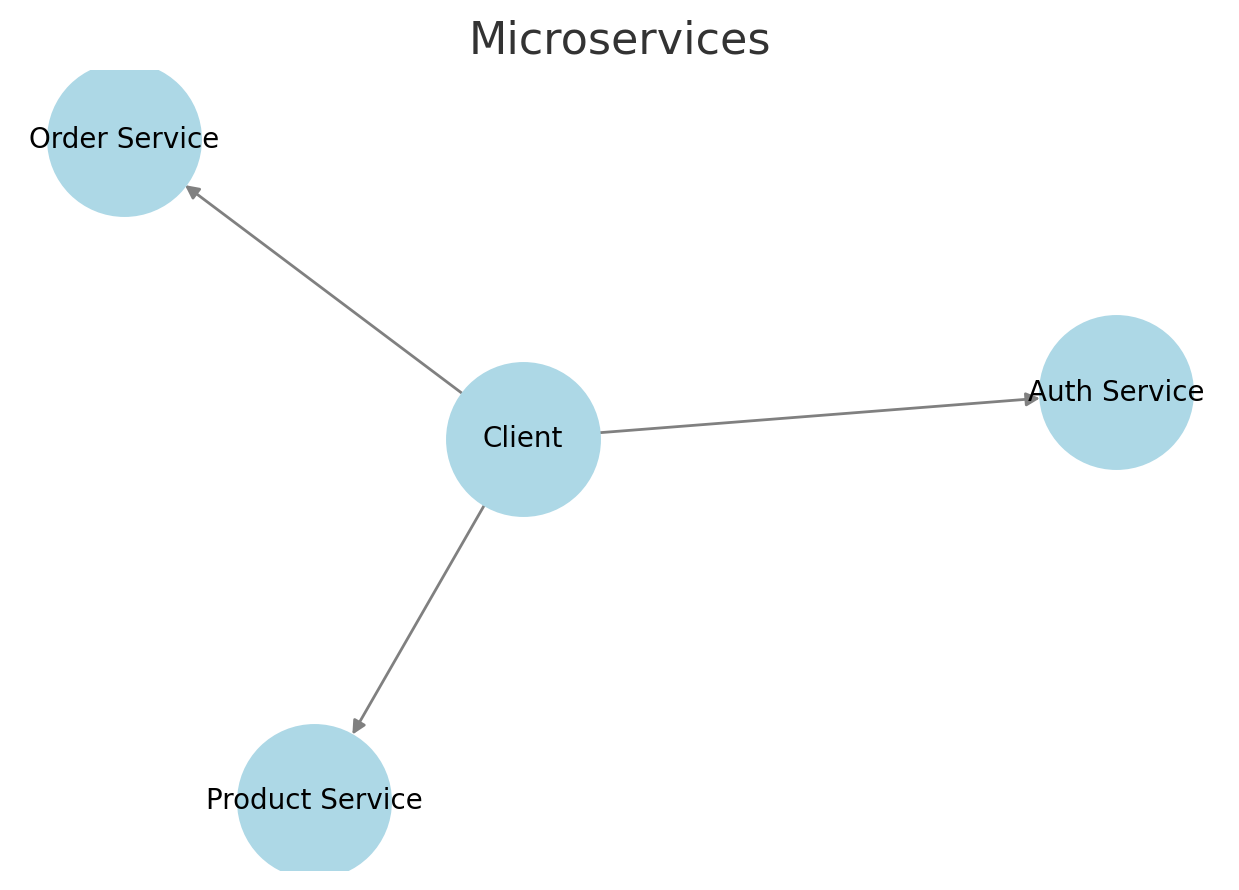
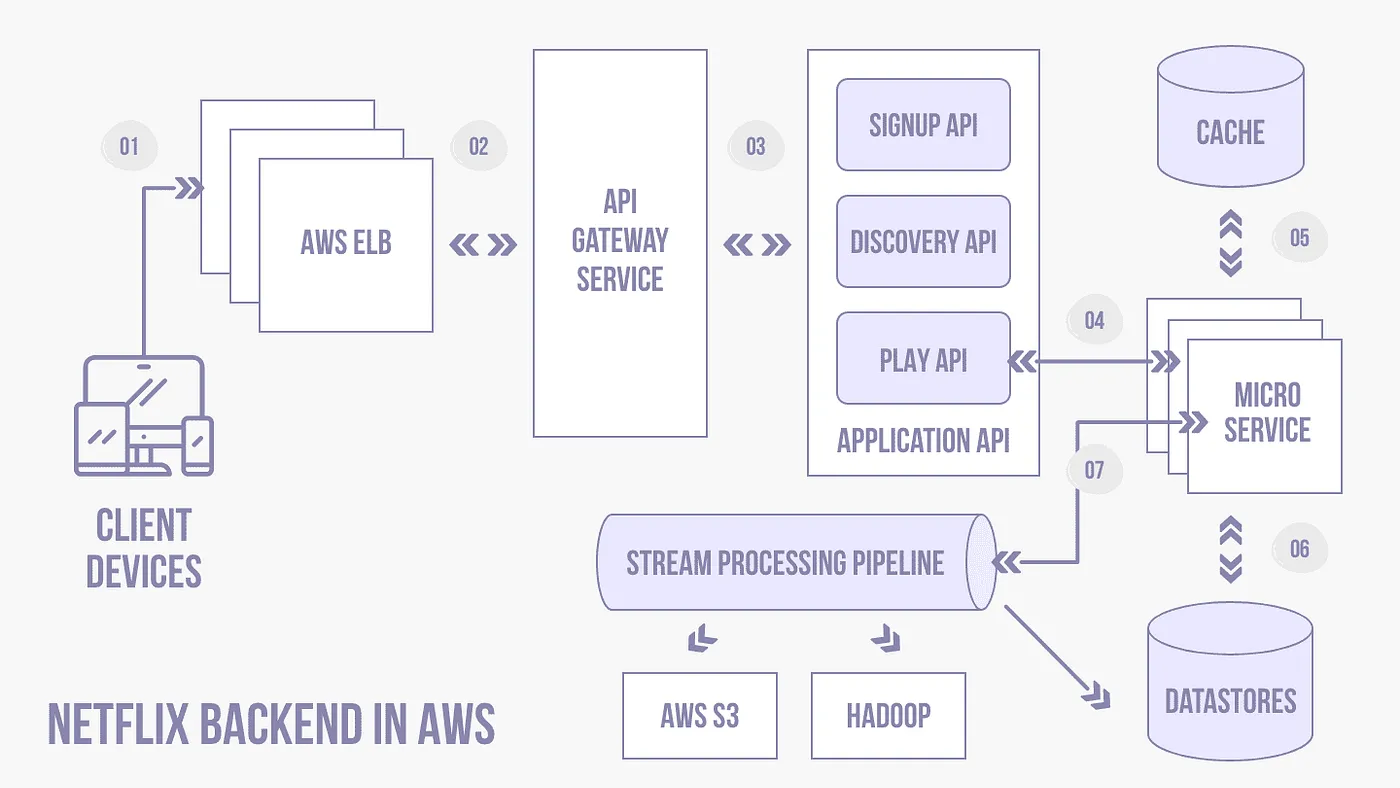
Netflix: Independent microservices for streaming, recommendations, and user authentication.
3. Event-Driven Architecture
- Description: Uses events as the primary way components communicate, making systems more decoupled.
- Examples:
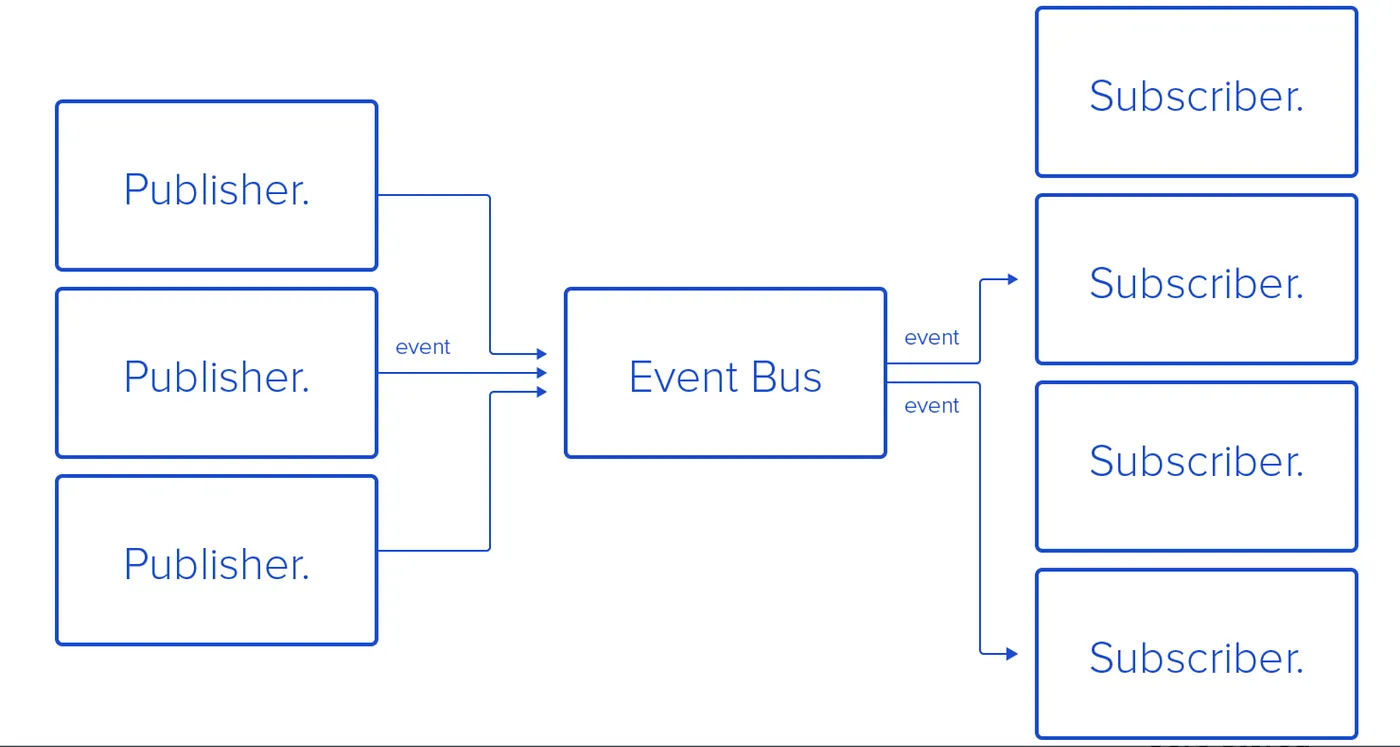
Publish-Subscribe Pattern: Message brokers like Kafka or RabbitMQ distribute events to interested subscribers.
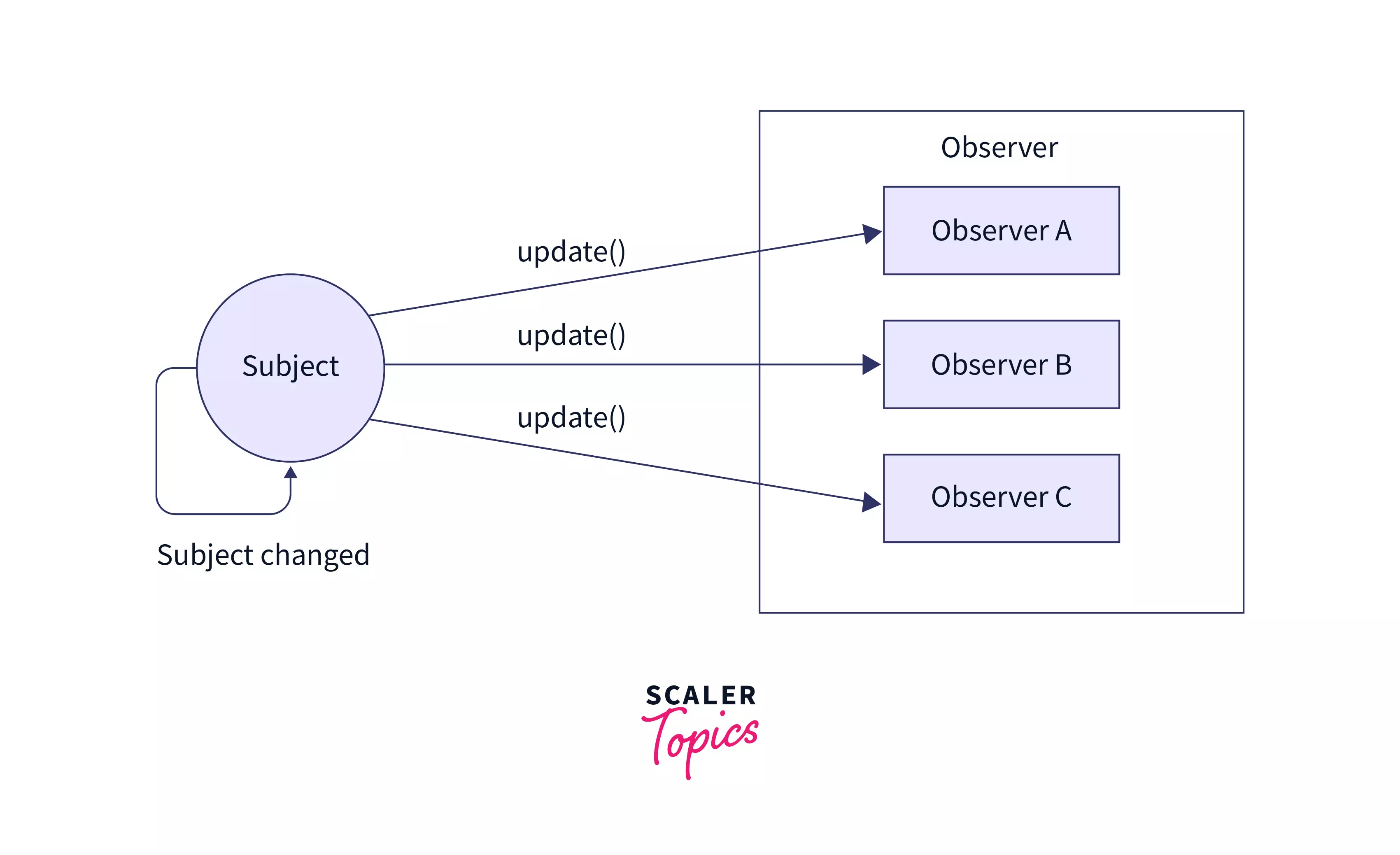
Observer Pattern: In GUI applications, UI elements react to user actions like button clicks. Social media like Facebook, Instigram, X.
4. Client-Server Architecture
- Description: A system where multiple clients request and receive services from a centralized server.
- Examples:
Web Applications: A browser (client) requests a web page from a server.
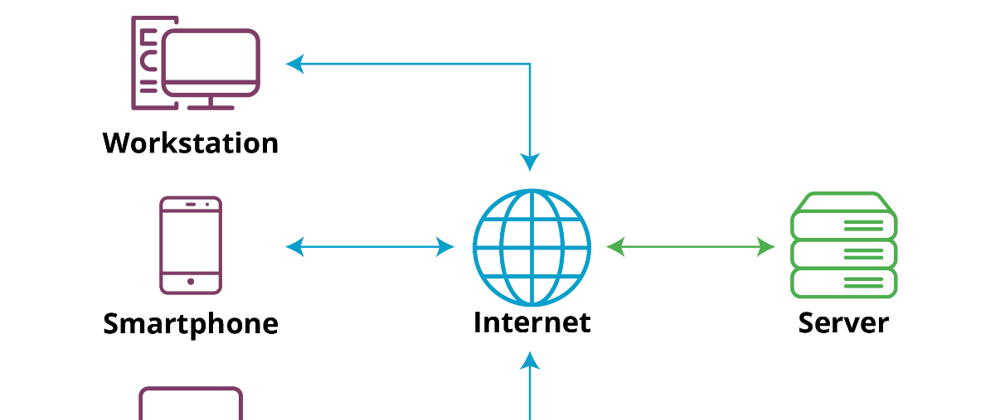
Database Systems: A client application sends SQL queries to a database server.
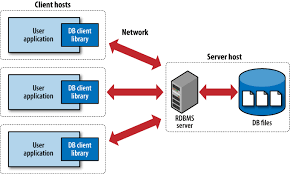
5. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture
- Description: Every node (peer) acts as both a client and a server, sharing resources.
- Examples:
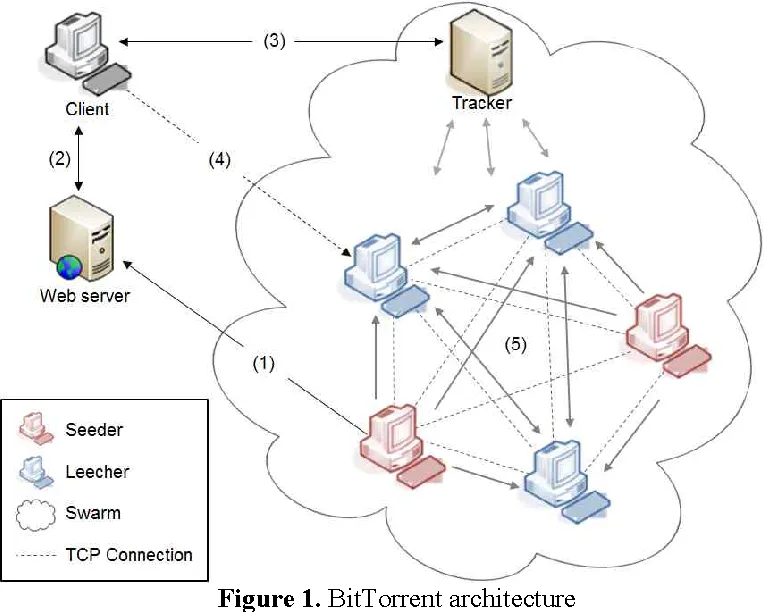
BitTorrent: Distributes file-sharing tasks across multiple peers.
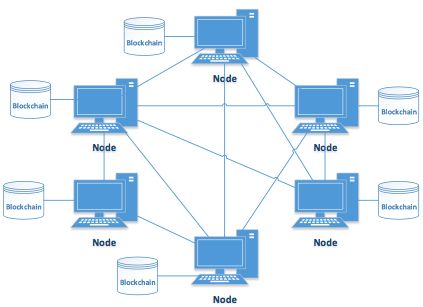
Blockchain Networks: Nodes validate transactions in a decentralized manner.
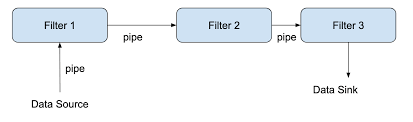
6. Pipe-and-Filter Architecture
- Description: A series of data processing components (filters) connected by pipes.
- Examples:
- UNIX Command Line:
cat file.txt | grep "error" | sort - Data Processing Pipelines: ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) systems for data warehousing.
- UNIX Command Line:
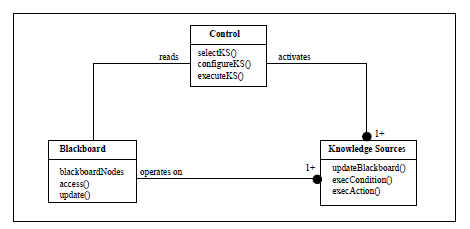
7. Blackboard Architecture
- Description: A shared knowledge base (blackboard) where different subsystems contribute to solving a problem.
- Examples:
- Speech Recognition: Multiple AI models contribute hypotheses to a central system.
- Autonomous Robotics: Sensors, vision processing, and decision-making modules work together.
8. Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- Description: Organizes software into reusable services that communicate via standardized protocols.
- Examples:
- Web Services (SOAP/REST APIs): Amazon’s AWS services expose functionalities as APIs.
- Enterprise Integration: Large companies integrate CRM, ERP, and payment processing systems.
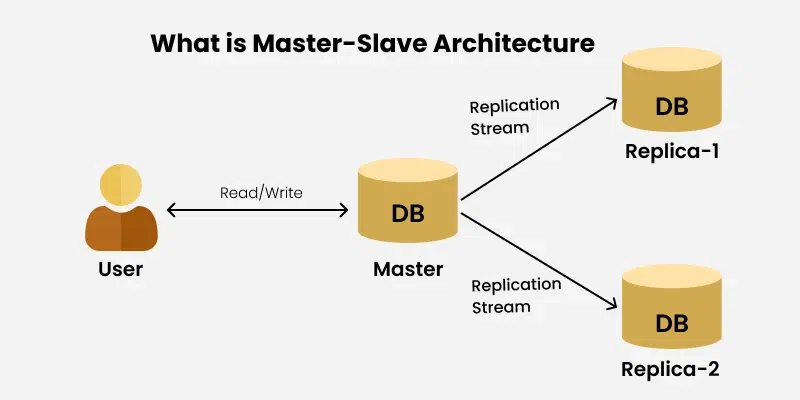
9. Master-Slave Architecture
- Description: A single master node controls multiple slave nodes, delegating tasks and synchronizing data.
- Examples:
Database Replication: MySQL master-slave setup where read operations use replicas.
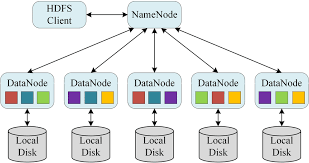
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): A master node (NameNode) manages storage nodes.
10. Component-Based Architecture
- Description: Applications are built from independent, reusable components.
- Examples:
Web Component Systems: React, Angular, or Vue.js UI components.
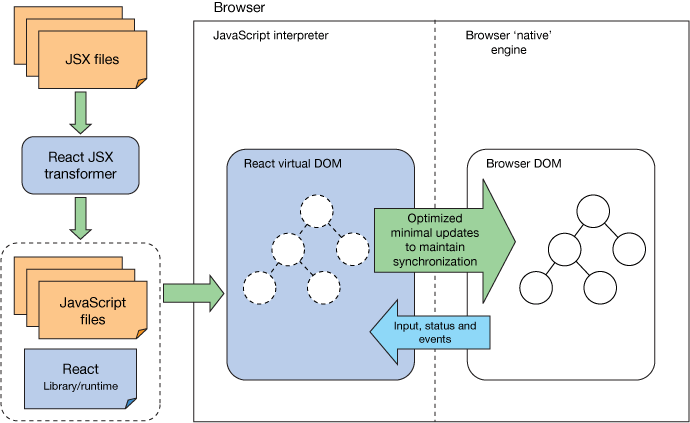
Enterprise Applications: JavaBeans or .NET components that provide modular functionality.
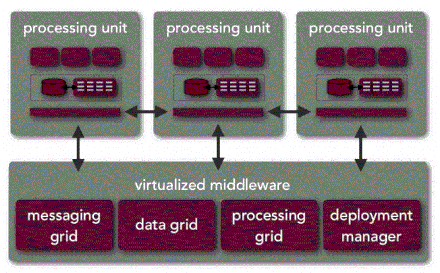
11. Space-Based Architecture
- Description: Uses distributed memory and processing to handle high scalability.
- Examples:
- Distributed Caching: Amazon DynamoDB, Redis caching layers.
- Grid Computing: Systems like Apache Ignite distribute processing across nodes.
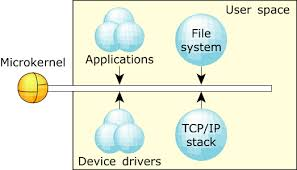
12. Microkernel (Plug-in) Architecture
- Description: A minimal core system that can be extended with plug-ins.
- Examples:
- Operating Systems: Linux with dynamically loaded kernel modules.
- Eclipse IDE: Core platform extended by plugins for different programming languages.