There are two ways to store a graph:
- Adjacency Matrix
- Adjacency List
Adjacency Matrix
In this method, the graph is stored in the form of the 2D matrix where rows and columns denote vertices. Each entry in the matrix represents the weight of the edge between those vertices.
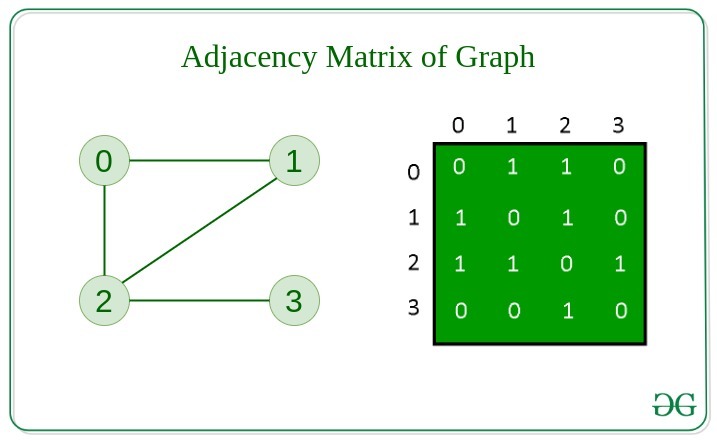
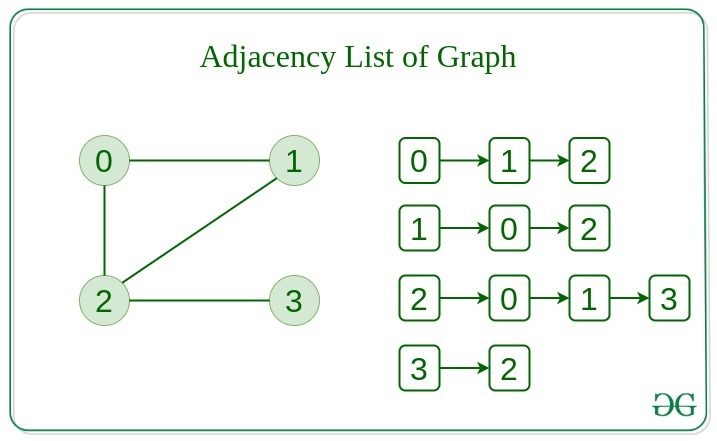
Adjacency List
This graph is represented as a collection of linked lists. There is an array of pointer which points to the edges connected to that vertex.
Comparison between Adjacency Matrix and Adjacency List
When the graph contains a large number of edges then it is good to store it as a matrix because only some entries in the matrix will be empty. An algorithm such as Prim’s and Dijkstra adjacency matrix is used to have less complexity.
| Action | Adjacency Matrix | Adjacency List |
|---|---|---|
| Adding Edge | O(1) | O(1) |
| Removing an edge | O(1) | O(N) |
| Initializing | O(N*N) | O(N) |
Basic Operations on Graphs
Below are the basic operations on the graph:
- Insertion of Nodes/Edges in the graph – Insert a node into the graph.
- Deletion of Nodes/Edges in the graph – Delete a node from the graph.
- Searching on Graphs – Search an entity in the graph.
- Traversal of Graphs – Traversing all the nodes in the graph.
Usage of graphs
- Maps can be represented using graphs and then can be used by computers to provide various services like the shortest path between two cities.
- When various tasks depend on each other then this situation can be represented using a Directed Acyclic graph and we can find the order in which tasks can be performed using topological sort.
- State Transition Diagram represents what can be the legal moves from current states. In-game of tic tac toe this can be used.
