A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority value. And, elements are served on the basis of their priority. That is, higher priority elements are served first.
Assigning Priority Value
Generally, the value of the element itself is considered for assigning the priority. For example,
The element with the highest value is considered the highest priority element. However, in other cases, we can assume the element with the lowest value as the highest priority element.
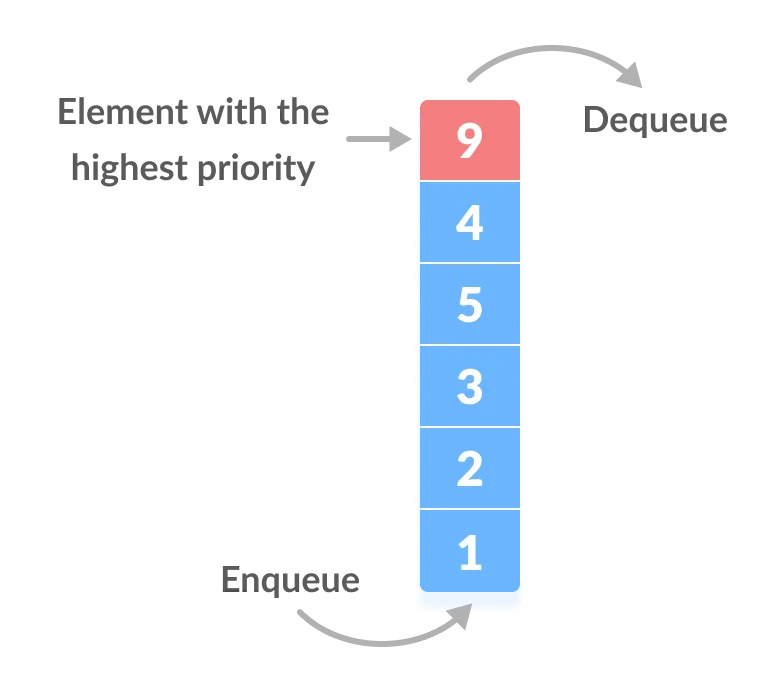
Priority Queue Operations
Basic operations of a priority queue are inserting, removing, and peeking elements.
Implementation of Priority Queue
Priority queue can be implemented using an array, a linked list, a heap data structure, or a binary search tree. Among these data structures, heap data structure provides an efficient implementation of priority queues.
How can we implement with a simple array or linked list? What is the big-O of each:
| Type | Add | Remove | Peek |
| Array | |||
| Linked List |
Using a Heap
Consider how a complete binary tree can be in stored in an array:
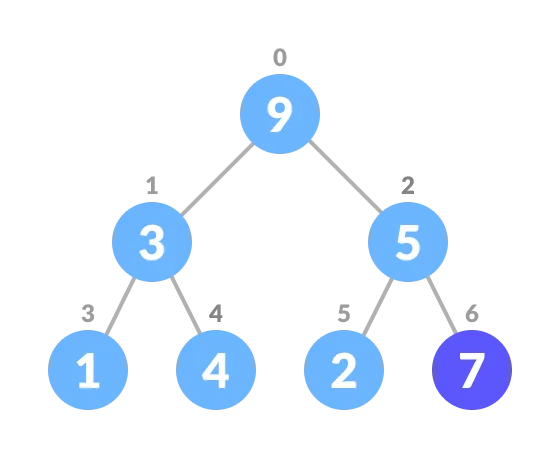
This can be:
| 9 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 |
So the parent of node i is node floor((i-1)/2)
Now lets think about what we can do!
Heap is a special case of balanced binary tree data structure where the root-node key is compared with its children and arranged accordingly. If α has child node β then −
key(α) ≥ key(β)
As the value of parent is greater than that of child, this property generates Max Heap. Based on this criteria, a heap can be of two types −
For Input → 35 33 42 10 14 19 27 44 26 31
Min-Heap − Where the value of the root node is less than or equal to either of its children.

Max-Heap − Where the value of the root node is greater than or equal to either of its children.

Both trees are constructed using the same input and order of arrival.
Adding elements:

Deleting Elements
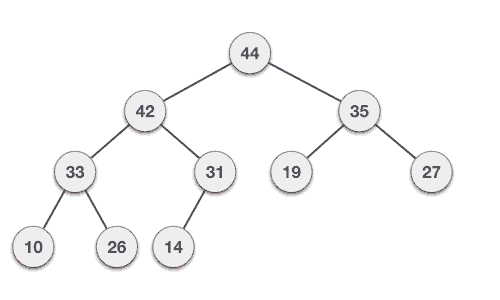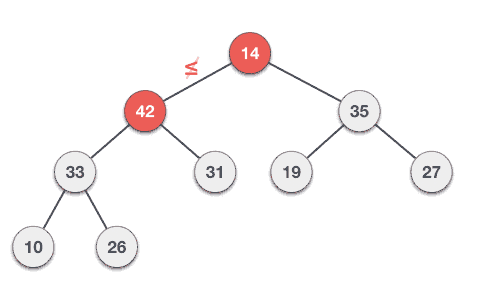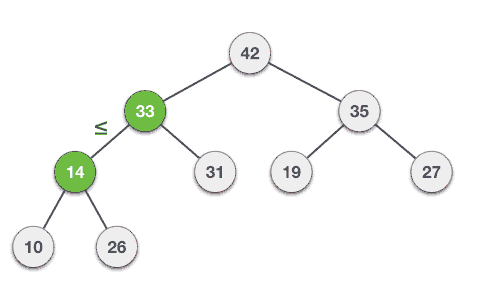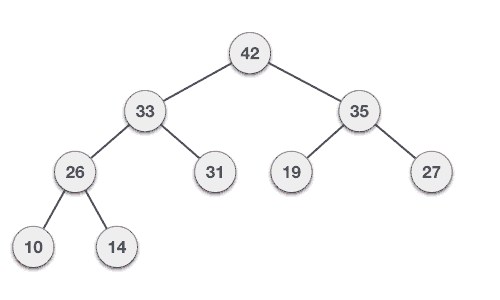
Max Heap Construction Algorithm
We shall use the same example to demonstrate how a Max Heap is created. The procedure to create Min Heap is similar but we go for min values instead of max values.
We are going to derive an algorithm for max heap by inserting one element at a time. At any point of time, heap must maintain its property. While insertion, we also assume that we are inserting a node in an already heapified tree.
Step 1 − Create a new node at the end of heap. Step 2 − Assign new value to the node. Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent. Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them. Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.
Note − In Min Heap construction algorithm, we expect the value of the parent node to be less than that of the child node.
Max Heap Deletion Algorithm
Let us derive an algorithm to delete from max heap. Deletion in Max (or Min) Heap always happens at the root to remove the Maximum (or minimum) value.
Step 1 − Remove root node. Step 2 − Move the last element of last level to root. Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent. Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them. Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.
Priority Queue code (repl):
// Priority Queue implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to swap position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree after adding a new element
void heapify(vector<int> &hT) {
int i = hT.size()-1;
int parent = floor((i-1)/2);
while (hT[i]>hT[parent]) {
swap(&hT[i],&hT[parent]);
if (parent == 0) {
break;
}
i = parent;
parent = floor((i-1)/2);
}
}
void heapifyDown(vector<int> &hT) {
int i = 0;
while (hT.size()-1>=(i*2)+1) {
int left = (i*2)+1;
int right = left+1;
if (hT[i]<=hT[left]) {
swap(&hT[i],&hT[left]);
i = left;
} else if (hT.size()-1>=right && hT[i]<=hT[right]) {
swap(&hT[i],&hT[right]);
i = right;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(vector<int> &hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.push_back(newNum);
} else {
hT.push_back(newNum);
heapify(hT);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(vector<int> &hT) {
for (int i = 0; i < hT.size(); ++i)
cout << hT[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
int peek(vector<int> &hT) {
return hT[0];
}
bool remove(vector<int> &hT) {
if (hT.size()<1) {
return false;
}
int value = hT[0];
hT[0] = hT[hT.size()-1];
hT.pop_back();
heapifyDown(hT);
return true;
}
bool empty(vector<int> &hT) {
return (hT.size()<1);
}
// Driver code
int main() {
vector<int> heapTree;
insert(heapTree, 3);
insert(heapTree, 4);
insert(heapTree, 9);
insert(heapTree, 5);
insert(heapTree, 2);
insert(heapTree, 12);
insert(heapTree, 7);
insert(heapTree, 10);
insert(heapTree, 14);
insert(heapTree, 1);
cout << "Max-Heap array: ";
printArray(heapTree);
while (!empty(heapTree)) {
cout << "Next: " << peek(heapTree) << endl;
remove(heapTree);
}
}priority_queue
The C++ STL includes a priority queue template implementation
github example code
