In Open Addressing, all elements are stored in the hash table itself. So at any point, size of table must be greater than or equal to total number of keys (Note that we can increase table size by copying old data if needed).
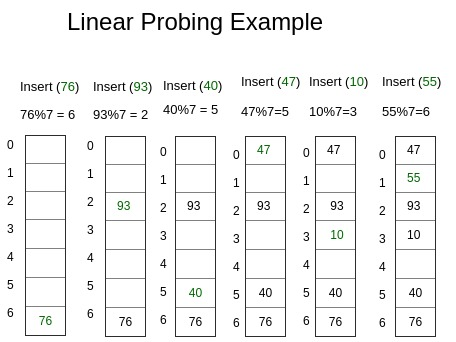
- Insert(k) – Keep probing until an empty slot is found. Once an empty slot is found, insert k.
- Search(k) – Keep probing until slot’s key doesn’t become equal to k or an empty slot is reached.
- Delete(k) – Delete operation is interesting. If we simply delete a key, then search may fail. So slots of deleted keys are marked specially as “deleted”.
Here, to mark a node deleted we have used dummy node with key and value -1.
Insert can insert an item in a deleted slot, but search doesn’t stop at a deleted slot.
The entire process ensures that for any key, we get an integer position within the size of the Hash Table to insert the corresponding value.
So the process is simple, user gives a (key, value) pair set as input and based on the value generated by hash function an index is generated to where the value corresponding to the particular key is stored. So whenever we need to fetch a value corresponding to a key that is just O(1).
Sample code (github)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// HashNode class for int to string mapping
class HashNode {
public:
int key;
string value;
// Constructor of HashNode
HashNode(int key, const string& value) : key(key), value(value) {}
};
// HashMap class for mapping integers to strings
class HashMap {
HashNode **arr;
int capacity;
int size;
HashNode *dummy;
public:
HashMap(int capacity = 20) : capacity(capacity), size(0) {
arr = new HashNode *[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++)
arr[i] = nullptr;
dummy = new HashNode(-1, "");
}
~HashMap() {
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (arr[i] && arr[i] != dummy)
delete arr[i];
}
delete[] arr;
delete dummy;
}
// Hash function for integer keys
int hashCode(int key) const {
return key % capacity;
}
// Function to add key-value pair
void insertNode(int key, const string& value) {
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
int startIndex = hashIndex;
// Linear probing to resolve collisions
while (arr[hashIndex] != nullptr && arr[hashIndex]->key != key &&
arr[hashIndex] != dummy) {
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % capacity;
if (hashIndex == startIndex) {
cout << "Hash table is full, cannot insert!" << endl;
return;
}
}
if (arr[hashIndex] == nullptr || arr[hashIndex] == dummy)
size++;
arr[hashIndex] = new HashNode(key, value);
}
// Function to delete a key-value pair
string deleteNode(int key) {
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
int startIndex = hashIndex;
while (arr[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
if (arr[hashIndex]->key == key) {
HashNode *temp = arr[hashIndex];
arr[hashIndex] = dummy;
size--;
string deletedValue = temp->value;
delete temp;
return deletedValue;
}
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % capacity;
if (hashIndex == startIndex) break;
}
cout << "Key not found!" << endl;
return "";
}
// Function to get the value for a given key
string get(int key) const {
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
int startIndex = hashIndex;
int counter = 0;
while (arr[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
if (counter++ > capacity) // to avoid infinite loop
return "";
if (arr[hashIndex]->key == key)
return arr[hashIndex]->value;
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % capacity;
if (hashIndex == startIndex) break;
}
return "";
}
// Return current size
int sizeofMap() const { return size; }
// Check if the table is empty
bool isEmpty() const { return size == 0; }
// Function to display the stored key-value pairs
void display() const {
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
if (arr[i] != nullptr && arr[i] != dummy)
cout << "key = " << arr[i]->key << ", value = " << arr[i]->value << endl;
}
}
};
// Driver method to test HashMap class
int main() {
HashMap hTable;
int key;
string value;
while (true) {
cout << "\n1. Add, 2. Lookup, 3. Delete, 4. Display, 5. Exit: ";
int opt;
cin >> opt;
cin.ignore(); // Ignore newline after option
if (opt == 1) {
cout << "Enter key (integer): ";
cin >> key;
cin.ignore();
cout << "Enter value (string): ";
getline(cin, value);
hTable.insertNode(key, value);
} else if (opt == 2) {
cout << "Enter key to lookup (integer): ";
cin >> key;
value = hTable.get(key);
if (!value.empty())
cout << "Found: " << value << endl;
else
cout << "Not found!" << endl;
} else if (opt == 3) {
cout << "Enter key to delete (integer): ";
cin >> key;
hTable.deleteNode(key);
} else if (opt == 4) {
hTable.display();
} else if (opt == 5) {
break;
} else {
cout << "Invalid option!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Complexity analysis for Insertion:
- Time Complexity:
- Best Case: O(1)
- Worst Case: O(N). This happens when all elements have collided and we need to insert the last element by checking free space one by one.
- Average Case: O(1) for good hash function, O(N) for bad hash function
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Complexity analysis for Deletion:
- Time Complexity:
- Best Case: O(1)
- Worst Case: O(N)
- Average Case: O(1) for good hash function; O(N) for bad hash function
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Complexity analysis for Searching:
- Time Complexity:
- Best Case: O(1)
- Worst Case: O(N)
- Average Case: O(1) for good hash function; O(N) for bad hash function
- Auxiliary Space: O(1) for search operation
