A tree is a popular data structure that is non-linear in nature. Unlike other data structures like an array, stack, queue, and linked list which are linear in nature, a tree represents a hierarchical structure. The ordering information of a tree is not important. A tree contains nodes and 2 pointers. These two pointers are the left child and the right child of the parent node. Let us understand the terms of tree in detail.
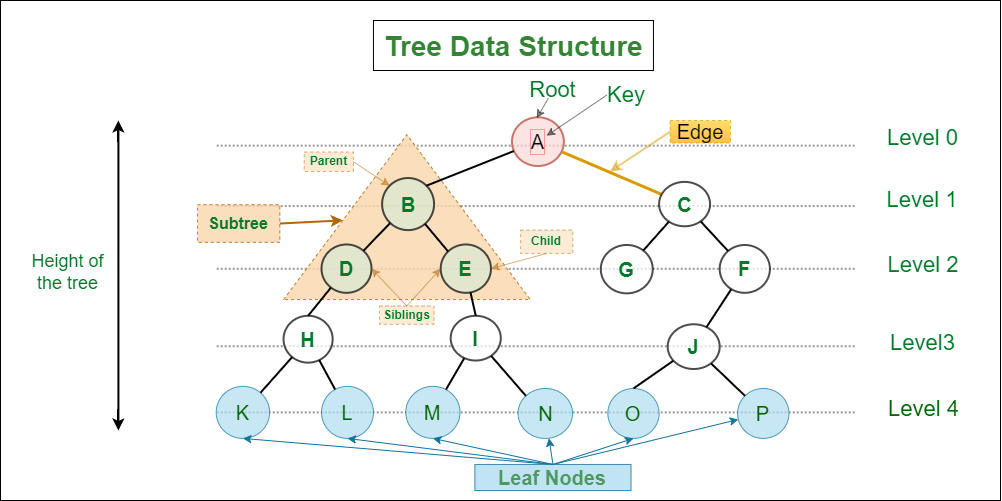
The main applications of tree data structure:
- Manipulate hierarchical data.
- Make information easy to search (see tree traversal).
- Manipulate sorted lists of data.
- As a workflow for compositing digital images for visual effects.
- Router algorithms
- Form of multi-stage decision-making (see business chess).
- Trees can be used to represent the structure of a sentence, and can be used in parsing algorithms to analyze the grammar of a sentence.
- Trees can be used to represent the decision-making process of computer-controlled characters in games, such as in decision trees.
- Huffman coding uses a tree to represent the frequency of characters in a text, which can be used for data compression.
- Trees are used to represent the syntax of a programming language, and can be used in compiler design to check the syntax of a program and generate machine code.
Definition: Binary Tree
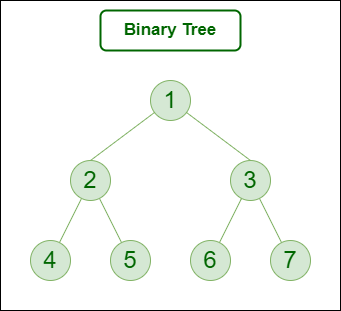
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node can have at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child. The topmost node in a binary tree is called the root, and the bottom-most nodes are called leaves. A binary tree can be visualized as a hierarchical structure with the root at the top and the leaves at the bottom.
Representation of Binary Tree:
Each node in the tree contains the following:
- Data
- Pointer to the left child
- Pointer to the right child
In C, we can represent a tree node using structures. In other languages, we can use classes as part of their OOP feature. Below is an example of a tree node with integer data.
// Use any below method to implement Nodes of tree
// Method 1: Using "struct" to make
// user-define data type
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Method 2: Using "class" to make
// user-define data type
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
Basic Operations On Binary Tree:
- Inserting an element.
- Removing an element.
- Searching for an element.
- Deletion for an element.
- Traversing an element. There are four (mainly three) types of traversals in a binary tree which will be discussed ahead.
Auxiliary Operations On Binary Tree:
- Finding the height of the tree
- Find the level of the tree
- Finding the size of the entire tree.
Applications of Binary Tree:
- In compilers, Expression Trees are used which is an application of binary trees.
- Huffman coding trees are used in data compression algorithms.
- Priority Queue is another application of binary tree that is used for searching maximum or minimum in O(1) time complexity.
- Represent hierarchical data.
- Used in editing software like Microsoft Excel and spreadsheets.
- Useful for indexing segmented at the database is useful in storing cache in the system,
- Syntax trees are used for most famous compilers for programming like GCC, and AOCL to perform arithmetic operations.
- For implementing priority queues.
- Used to find elements in less time (binary search tree)
- Used to enable fast memory allocation in computers.
- Used to perform encoding and decoding operations.
- Binary trees can be used to organize and retrieve information from large datasets, such as in inverted index and k-d trees.
- Binary trees can be used to represent the decision-making process of computer-controlled characters in games, such as in decision trees.
- Binary trees can be used to implement searching algorithms, such as in binary search trees which can be used to quickly find an element in a sorted list.
- Binary trees can be used to implement sorting algorithms, such as in heap sort which uses a binary heap to sort elements efficiently.
