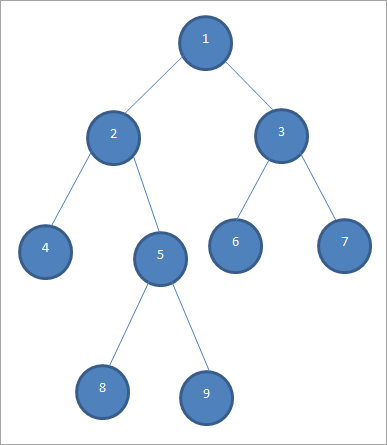
1. Sequential representation:
In this representation, array structure is used to implement the tree. Size of array is equal to the total nodes in the tree, index of root node is 0. If a node is at ‘i’ location then its left child is at ‘2i’ index and right child at ‘2i + 1’ location in the array. Visual Representation: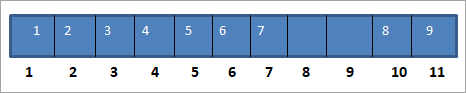
Linked-list Representation:
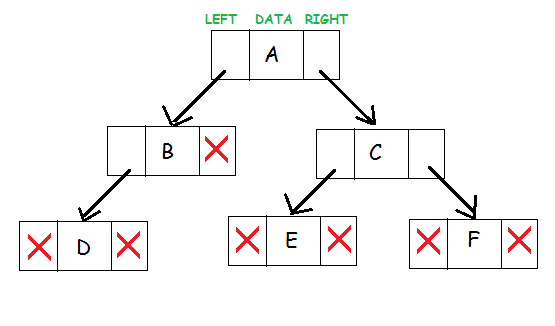
As you can see, the topmost node is the parent node of nodes “B” and “C”. Each node contains a pointer to the left subtree and pointer to the right subtree. Node A has a pointer to the left child that is B and a pointer pointing to the right child of A that is B. Middle box represents the data in the node. The nodes which doesn’t have a child are called ass leaf nodes. These nodes do not have pointer to their subtrees. Therefore left and right pointers are set to NULL.
To implement binary tree, we will define the conditions for new data to enter into our tree.
