Here’s a complete example of constructing a Huffman Tree for a code with 6 characters. We’ll walk through the process step-by-step, including the tree construction and the final codes for each character.
Input Characters and Frequencies
| Character | Frequency |
|---|---|
| A | 5 |
| B | 9 |
| C | 12 |
| D | 13 |
| E | 16 |
| F | 45 |
Step 1: Initialize Priority Queue
Each character is treated as a leaf node in the tree. We’ll use a priority queue (min-heap) to store the nodes, sorted by frequency.
Initial Priority Queue:
[A:5, B:9, C:12, D:13, E:16, F:45]
Step 2: Build the Huffman Tree
Iteration 1: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
A:5andB:9(smallest frequencies). - Create a new node with
frequency = 5 + 9 = 14and childrenAandB.
Updated Priority Queue:
[C:12, D:13, E:16, F:45, (AB):14]
Iteration 2: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
C:12andD:13. - Create a new node with
frequency = 12 + 13 = 25and childrenCandD.
Updated Priority Queue:
[E:16, F:45, (AB):14, (CD):25]
Iteration 3: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
(AB):14andE:16. - Create a new node with
frequency = 14 + 16 = 30and children(AB)andE.
Updated Priority Queue:
[F:45, (CD):25, (ABE):30]
Iteration 4: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
(CD):25and(ABE):30. - Create a new node with
frequency = 25 + 30 = 55and children(CD)and(ABE).
Updated Priority Queue:
[F:45, (CDEAB):55]
Iteration 5: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
F:45and(CDEAB):55. - Create a new node with
frequency = 45 + 55 = 100and childrenFand(CDEAB).
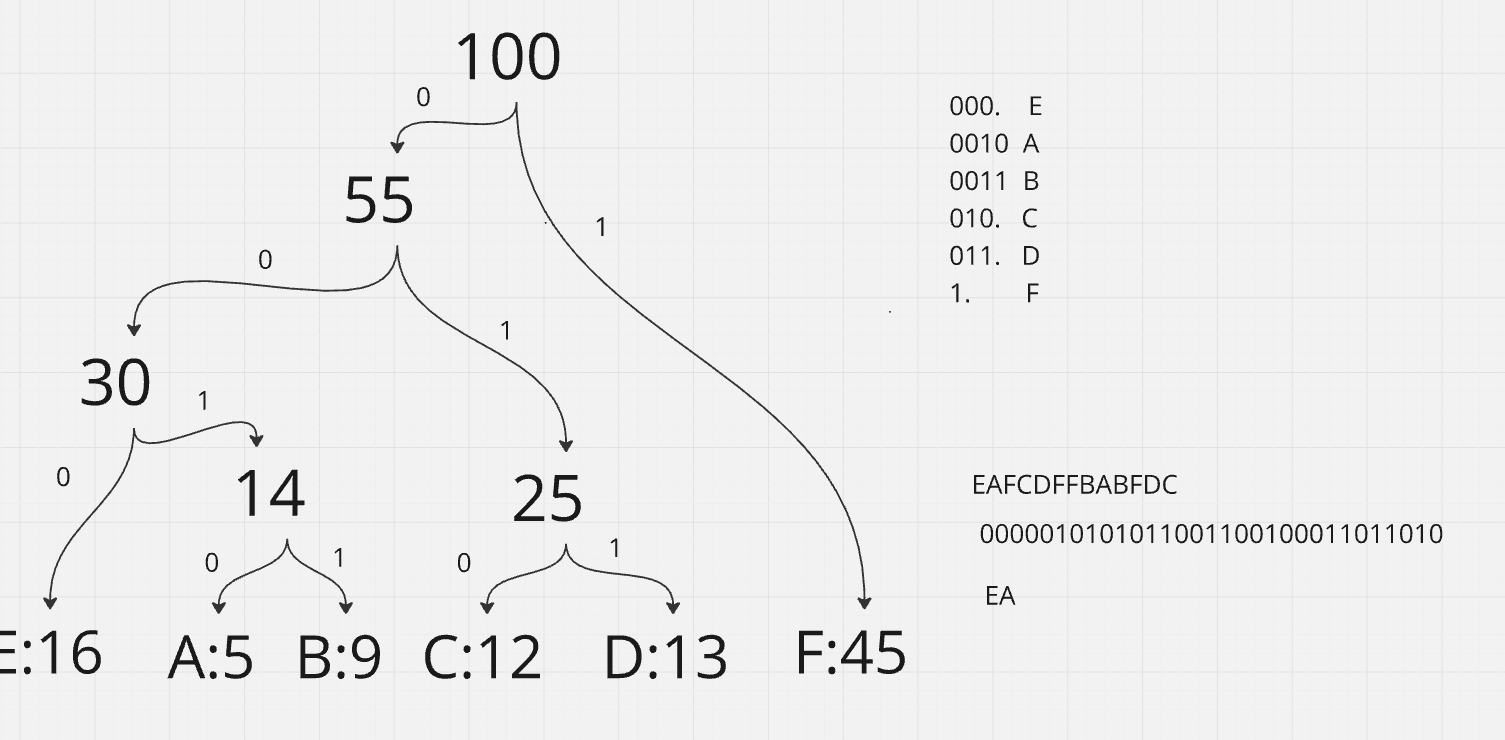
Final Huffman Tree Root:
[(F):45, (CDEAB):55] -> Root
Step 3: Assign Codes
Now traverse the Huffman Tree to assign binary codes:
- Assign
0to the left child and1to the right child recursively.
Tree Structure:
(Root: 100)
/ \
(F: 45) (CDEAB: 55)
/ \
(CD: 25) (ABE: 30)
/ \ / \
(C:12) (D:13) (AB:14) (E:16)
/ \
(A:5) (B:9)
Codes:
F -> 0
C -> 100
D -> 101
A -> 1100
B -> 1101
E -> 111
Step 4: Output the Huffman Codes
| Character | Code |
|---|---|
| A | 1100 |
| B | 1101 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 101 |
| E | 111 |
| F | 0 |
Benefits of Huffman Coding
Huffman coding minimizes the total length of the encoded message by assigning shorter codes to more frequent characters and longer codes to less frequent ones. This makes it highly efficient for compression tasks.
Resulting codes:
Here’s a complete example of constructing a Huffman Tree for a code with 6 characters. We’ll walk through the process step-by-step, including the tree construction and the final codes for each character.
Input Characters and Frequencies
| Character | Frequency |
|---|---|
| A | 5 |
| B | 9 |
| C | 12 |
| D | 13 |
| E | 16 |
| F | 45 |
Step 1: Initialize Priority Queue
Each character is treated as a leaf node in the tree. We’ll use a priority queue (min-heap) to store the nodes, sorted by frequency.
mathematicaCopy codeInitial Priority Queue:
[A:5, B:9, C:12, D:13, E:16, F:45]
Step 2: Build the Huffman Tree
Iteration 1: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
A:5andB:9(smallest frequencies). - Create a new node with
frequency = 5 + 9 = 14and childrenAandB.
Updated Priority Queue:
mathematicaCopy code[C:12, D:13, E:16, F:45, (AB):14]
Iteration 2: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
C:12andD:13. - Create a new node with
frequency = 12 + 13 = 25and childrenCandD.
Updated Priority Queue:
csharpCopy code[E:16, F:45, (AB):14, (CD):25]
Iteration 3: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
(AB):14andE:16. - Create a new node with
frequency = 14 + 16 = 30and children(AB)andE.
Updated Priority Queue:
csharpCopy code[F:45, (CD):25, (ABE):30]
Iteration 4: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
(CD):25and(ABE):30. - Create a new node with
frequency = 25 + 30 = 55and children(CD)and(ABE).
Updated Priority Queue:
csharpCopy code[F:45, (CDEAB):55]
Iteration 5: Combine Two Smallest Nodes
- Remove
F:45and(CDEAB):55. - Create a new node with
frequency = 45 + 55 = 100and childrenFand(CDEAB).
Final Huffman Tree Root:
cssCopy code[(F):45, (CDEAB):55] -> Root
Step 3: Assign Codes
Now traverse the Huffman Tree to assign binary codes:
- Assign
0to the left child and1to the right child recursively.
lessCopy codeTree Structure:
(Root: 100)
/ \
(F: 45) (CDEAB: 55)
/ \
(CD: 25) (ABE: 30)
/ \ / \
(C:12) (D:13) (AB:14) (E:16)
/ \
(A:5) (B:9)
Codes:
F -> 0
C -> 100
D -> 101
A -> 1100
B -> 1101
E -> 111
Step 4: Output the Huffman Codes
| Character | Code |
|---|---|
| A | 1100 |
| B | 1101 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 101 |
| E | 111 |
| F | 0 |
