coLearn-AI is a web-based learning platform designed to support small-group, collaborative learning with structured activities, guided assessment, and AI-assisted feedback.
It is inspired by evidence-based pedagogies such as POGIL, team-based learning, and case-based instruction, and is designed to work equally well for:
- in-class group activities
- formative quizzes
- summative tests
- AI-guided reflection and follow-up
The system emphasizes thinking together, not just submitting answers.
Some Useful LInk
- Instructor Walk through
- Collabortive Activity Workflow
- Evaluation Activities (Quizzes and Tests)
- Authoring Langauge
Core Goals
- Support collaborative problem solving in small groups (1–4 students)
- Make activities explicitly structured, not ad-hoc
- Allow instructors to author once and reuse across contexts
- Provide immediate feedback without replacing instructor judgment
- Enable AI-assisted guidance while preserving academic integrity
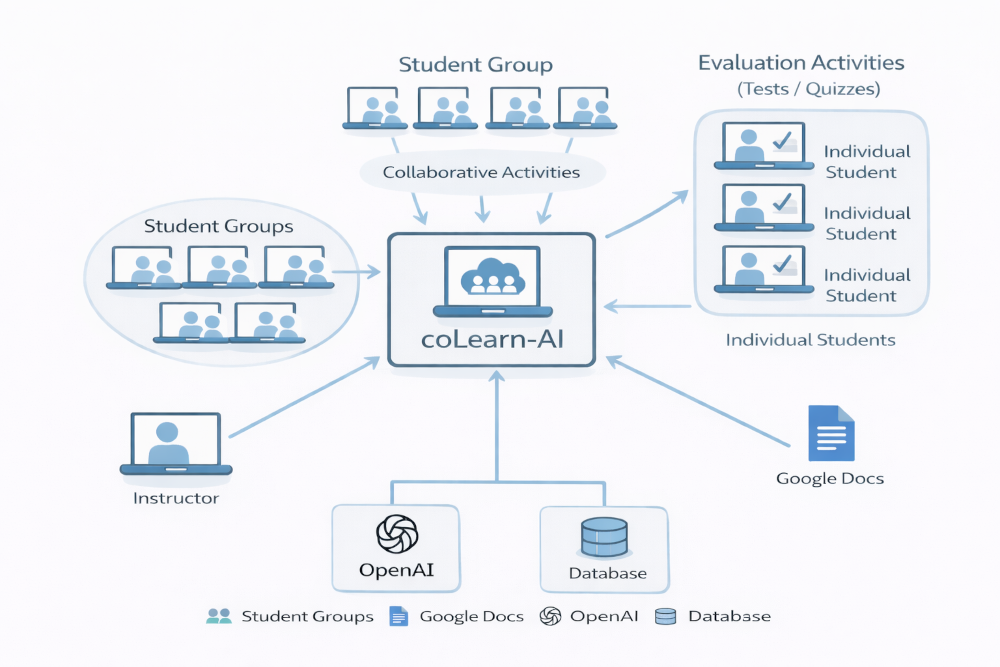
At a high level:
- Instructor authors an activity
- Using a simple, readable text-based format
- Stored in Google Docs or Sheets
- Instructor launches the activity
- Students are grouped automatically
- Each group gets its own activity instance
- Students work collaboratively
- One active student at a time (rotates automatically)
- Others observe and discuss
- Responses are saved incrementally
- Completed sections lock
- Progress is preserved
- AI support (optional)
- Evaluates completeness
- Generates follow-up prompts
- Never overwrites student work
Key Design Choice: One Activity = One Group
Unlike many LMS tools:
- Each group runs its own instance of the activity
- Responses are group-level, not individual
- The system tracks:
- progress
- completion
- participation
- active student rotation
This models how collaborative learning actually happens in the classroom.
Authoring Format (Instructor-Friendly)
Activities are written in a structured markup format that is:
- readable as plain text
- easy to version and revise
- parseable by the system
- independent of the UI
Example
\title{Clinical Reasoning: Chest Pain}
\studentlevel{Medical School – Pre-Clinical}
\activitycontext{
In this activity, your group will reason through a brief
clinical scenario involving chest pain.
}
\questiongroup{Initial Assessment}
\question{
A 54-year-old patient presents with chest pain.
List three immediate questions you would ask.
}
\textresponse{5}
\sampleresponses{
Onset, character, radiation of pain;
associated symptoms such as dyspnea or diaphoresis;
past cardiac history.
}
\feedbackprompt{
Does the explanation justify urgency and diagnostic value?
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Why this matters
- Faculty can focus on pedagogy, not UI mechanics
- Activities can be:
- collaborative
- quiz-like
- test-like
- The same activity can run:
- in class
- asynchronously
- with or without AI assistance
Two Modes: Activities and Tests
Collaborative Activities
- Students work in groups
- One active participant at a time
- Discussion encouraged
- AI can prompt deeper reasoning
Tests
- Individual
- Timed or untimed
- No AI assistance
- Same authoring format
This allows instructional continuity across learning modes.
Why This Matters
- Encourages clinical reasoning, not memorization
- Makes thinking visible
- Supports formative assessment
- Reduces grading load without automating judgment
- Preserves instructor control
